There are many different types of colleges in the U.S., and it can be confusing as a student to understand the differences between them and find out which is best for you. We have put together a simple guide to differentiate between the main types of colleges, universities, and career colleges:
Types of Colleges in the U.S. – Search for Colleges Here
Liberal Arts Colleges and Universities
Private 4-Year and 2-Year
Earn a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher
Study wide range of courses
These colleges offer a broad base of courses in the liberal arts — literature, philosophy, history, languages, mathematics, humanities, and social and natural sciences. They typically offer four-year programs that lead to a bachelor’s degree; students usually take courses in a range of subjects during their first two years and then choose a major. These colleges prepare you for a variety of careers, as well as for graduate work in many fields, including professions such as law, medicine and business.
Universities may offer more majors than Liberal Art Colleges such as engineering, architecture, health and other programs. At most universities, you can earn bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees. Most universities contain several smaller colleges; for example, colleges of agriculture, teaching, and liberal arts. You may have to apply to a specific college within the university and take most of your classes within that college. At a university, you can prepare for many types of careers or for further study in graduate school.
Community Colleges
2-Year College
Earn an Associate’s Degree
Affordable, prepare you for career or 4-Year institution
These colleges prepare you to continue your education or to enter the workforce immediately. They offer associate degrees and certificate of completion, which get you ready to transfer to a four-year college and earn a bachelor’s degree.
Community colleges are often an affordable and convenient option; they charge relatively low tuition to in-state residents. Many students can also save money by living at home.
Career Colleges or Vo-Tech
Career focused, not required to take Gen-Ed courses
Earn an Certificate of Completion or Associates Degree
Career readiness
A vo-tech or career college offers specialized training to students who are interested in a particular industry or career. You take classes only in your field of study — for example, culinary arts, firefighting, dental hygiene or medical-records technology.
Student Population by College Type
*data pulled from The Chronicle of Higher Education Almanac Issue 2011-2012
Type of Colleges
There are many different types of colleges in the U.S., and it can be confusing as a student to understand the differences between them and find out which is best for you. We have put together a simple guide to differentiate between the main types of colleges, universities, and career colleges:
Types of Colleges in the U.S. – Search for Colleges Here
Liberal Arts Colleges and Universities
These colleges offer a broad base of courses in the liberal arts — literature, philosophy, history, languages, mathematics, humanities, and social and natural sciences. They typically offer four-year programs that lead to a bachelor’s degree; students usually take courses in a range of subjects during their first two years and then choose a major. These colleges prepare you for a variety of careers, as well as for graduate work in many fields, including professions such as law, medicine and business.
Universities
Universities may offer more majors than Liberal Art Colleges such as engineering, architecture, health and other programs. At most universities, you can earn bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees. Most universities contain several smaller colleges; for example, colleges of agriculture, teaching, and liberal arts. You may have to apply to a specific college within the university and take most of your classes within that college. At a university, you can prepare for many types of careers or for further study in graduate school.
Community Colleges
These colleges prepare you to continue your education or to enter the workforce immediately. They offer associate degrees and certificate of completion, which get you ready to transfer to a four-year college and earn a bachelor’s degree.
Community colleges are often an affordable and convenient option; they charge relatively low tuition to in-state residents. Many students can also save money by living at home.
Career Colleges or Vo-Tech
A vo-tech or career college offers specialized training to students who are interested in a particular industry or career. You take classes only in your field of study — for example, culinary arts, firefighting, dental hygiene or medical-records technology.
Student Population by College Type
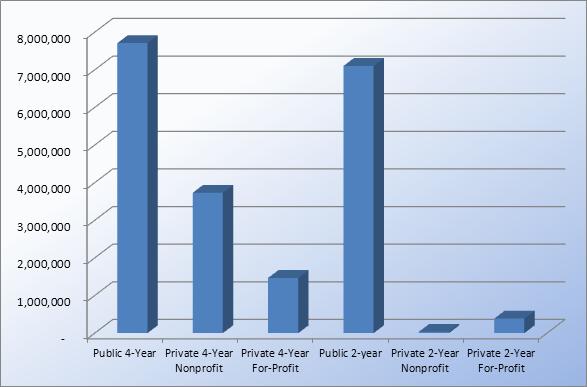
*data pulled from The Chronicle of Higher Education Almanac Issue 2011-2012
Share this post: